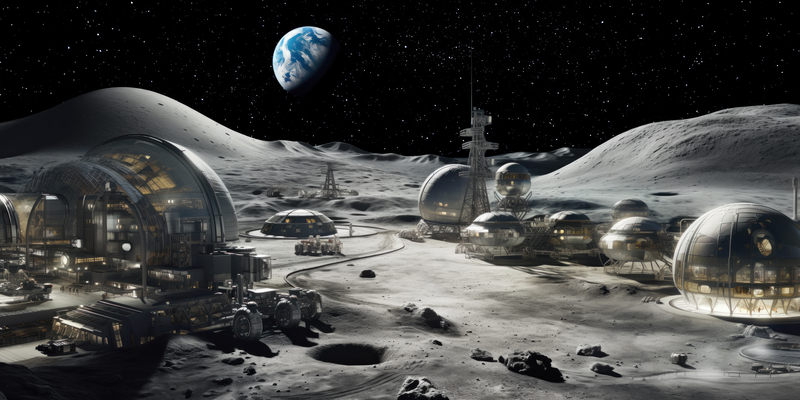

Chinese language officers have revealed extra particulars of its plan to construct an Worldwide Lunar Analysis Station (ILRS) on the Moon.
The intention is to construct a base close to the satellite tv for pc’s south pole on the centre of a 100km-radius zone of investigation. The deadline for this ingredient of the scheme is 2035. By 2050, the ILRS will develop right into a community of analysis services on the Moon’s stretching to the equator and the “far facet”.
It will embrace communications programs, energy technology and different infrastructure. An idea animation was launched by the China Nationwide House Administration, and might be seen right here:
First proposed by China and Russia in 2017, the ILRS will primarily be operated by autonomous robots of 1 variety or one other, with people dropping in for brief stays.
An area station will even be positioned in lunar orbit to function a transport hub for supplies passing backwards and forwards between the Moon and Earth.
The plans have been outlined by Wu Yanhua, the vice administrator of China Nationwide House Administration and the lead designer of its house exploration programme. He was talking final Thursday on the Deep House Exploration Convention, which is being held within the metropolis of Huangshan in east-central China.
In a press assertion, the State Council of the Folks’s Republic mentioned the initiative was “paving the best way for a brand new period of worldwide house collaboration, drawing in creating international locations with out their very own house missions and igniting widespread enthusiasm for participation”.
In preparation for the development of the bases, China is poised to launch quite a few missions to the lunar south pole. These will comprise the Chang’e-7 mission in 2026 and Chang’e-8 in 2028.
Chang’e-7 will carry a hopper designed to seek for water ice within the shadowed craters, and Chang’e-8 will attempt to discover out what might be completed with in situ assets, reminiscent of whether or not bricks might be printed from lunar mud.
The South China Morning Submit reported yesterday that Chinese language scientists plan to ship bricks constituted of simulated lunar soil into house to check whether or not they can be utilized to construct the bottom.
They are going to be despatched into the house from the Tiangong house station subsequent month on the Tianzhou-8 cargo spacecraft.
In a three-year experiment, scientists will observe how the samples degrade underneath radiation and temperature adjustments.
Ding Leiyun, a scientist at Hauzhong College of Science, advised the paper: “We will bake the bricks to a power of 100 megapascals right here on Earth, which is way tougher than concrete.”
The analysis, nevertheless, is required to find out whether or not they can stand up to the cruel atmosphere on the Moon.
Worldwide participation
Numerous different international locations are taking part within the programme. On Thursday, Senegal agreed to change into a co-developer of the programme, becoming a member of Russia, Venezuela, Belarus, Pakistan, Azerbaijan, South Africa, Egypt, Nicaragua, Thailand, Serbia and Kazakhstan.
Different organisations that signed memorandums of understanding in the course of the two-day convention included the South African Radio Astronomy Observatory, the House Science Innovation Centre of Panama, the Belgrade Observatory, the Nationwide College of Sciences and Expertise of Pakistan and the College of Bandar Lampung in Indonesia.
Moreover, firms such because the UAE’s Orbital House and Switzerland’s Spacetalk signed agreements.
In whole, China is hoping to draw 50 international locations, 500 analysis establishments, and 5,000 scientists over the subsequent 10 years.
- Subscribe right here to get tales about development around the globe in your inbox thrice every week.







